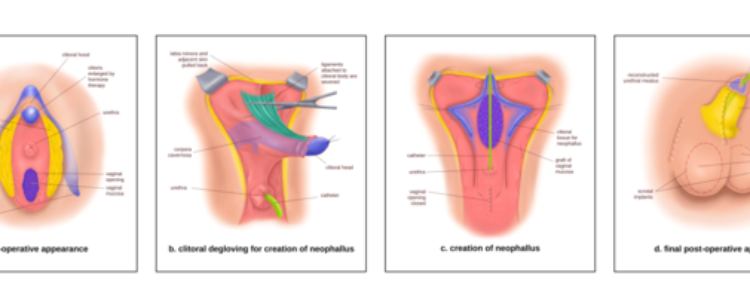
Bottom surgery for individuals transitioning from female to male, also known as phalloplasty or metoidioplasty, aims to create male genitalia. The specific results of bottom surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the surgical technique chosen, individual anatomy, healing process, and personal goals. It’s important to note that the decision to undergo bottom surgery is deeply personal, and the results can vary from person to person. Here are some general considerations regarding the results of female to male bottom surgery:
- Phalloplasty: Phalloplasty is a surgical procedure that involves constructing a neophallus (new penis) using different techniques. The surgical process typically involves taking tissue grafts from donor sites such as the forearm, thigh, or abdomen to create the phallus. The neophallus can vary in size, appearance, and sensation based on the individual’s preferences and surgical technique chosen. It’s important to discuss specific goals and expectations with a qualified surgeon.
- Metoidioplasty: Metoidioplasty is another surgical option for individuals transitioning from female to male. It involves releasing the ligament that restricts the clitoris’ growth due to testosterone hormone therapy. This procedure allows the enlarged clitoris, known as the neopenis, to resemble a small penis. The results of metoidioplasty can vary depending on the individual’s starting anatomy, hormonal changes, and desired outcome.
- Sensation and Function: The level of sensation and sexual function after bottom surgery can vary. Some individuals report increased sensitivity in the neophallus or neopenis, while others may experience less sensation. Achieving erections and urinary function can also depend on the surgical technique chosen. It’s important to discuss potential outcomes and limitations with your surgeon before the procedure.
- Scarring and Healing: Like any surgical procedure, bottom surgery for female to male transition involves incisions and healing. Scarring will occur, and the appearance of scars can vary depending on individual healing processes, surgical techniques, and post-operative care. It’s important to follow post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon to optimize healing and minimize complications.
- Revision Surgeries: It’s important to note that additional surgeries, called revision surgeries, may be necessary to refine or adjust the results of bottom surgery. These revision surgeries can address concerns such as aesthetic improvements, scar revisions, or adjustments to the size or positioning of the neophallus. Discussing potential revision surgeries with the surgeon during the initial consultations is recommended.
It’s essential to consult with experienced and qualified surgeons who specialize in transgender healthcare to discuss your specific goals, options, and potential outcomes of bottom surgery. Surgeons can provide personalized information, discuss risks and benefits, and address any concerns you may have. They will guide you through the process and help you make informed decisions based on your individual circumstances and desired outcomes.
Bottom surgery for female-to-male (FTM) transgender people is a complex and individualized process. There are two main types of bottom surgery for FTM people: metoidioplasty and phalloplasty.
- Metoidioplasty is a surgery that uses the existing tissue of the clitoris to create a larger, more visible phallus. It does not involve the creation of a urethra, so urination will still occur through the vagina. Metoidioplasty is typically a one-stage surgery with a shorter recovery time than phalloplasty.
- Phalloplasty is a more complex surgery that involves the creation of a penis from tissue from another part of the body, such as the arm or thigh. It can also involve the creation of a urethra and scrotum. Phalloplasty is typically a two-stage surgery with a longer recovery time than metoidioplasty.
The risks of bottom surgery for FTM people include bleeding, infection, and nerve damage. There is also a risk of complications specific to each type of surgery, such as the need for revisions or the inability to achieve an erection after phalloplasty.
The success rate of bottom surgery for FTM people is very high. A study published in the journal “Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery” found that 99.7% of trans people who had undergone bottom surgery experienced a degree of satisfaction with the outcome.
If you are considering bottom surgery, it is important to talk to a qualified surgeon about your options and the risks and benefits of each procedure. You should also make sure that you are emotionally prepared for the surgery and the recovery process.
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
- The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH): https://www.wpath.org/
- The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS): https://www.plasticsurgery.org/
- The Human Rights Campaign: https://www.hrc.org/
Phalloplasty outcomes
Phalloplasty is a gender-affirming surgical procedure that involves constructing a neophallus (a surgically created penis) for individuals undergoing female-to-male (FTM) transition. The specific outcomes of phalloplasty can vary based on factors such as the surgical technique used, individual anatomy, and the goals of the patient. Here are some general considerations regarding phalloplasty outcomes:
- Phalloplasty Techniques:
-
- There are different techniques for phalloplasty, including radial forearm flap, anterolateral thigh flap, and pedicled or free flap options. The choice of technique can influence the final results.
- Neophallus Size and Appearance:
-
- The size and appearance of the neophallus are essential aspects of phalloplasty outcomes. Surgeons work closely with patients to determine the desired size, shape, and aesthetics of the neophallus.
- Urethral Lengthening:
-
- Many phalloplasty procedures include urethral lengthening to allow for standing urination. The success of this aspect of the surgery is crucial for functional outcomes.
- Sensation and Erectile Function:
-
- Achieving tactile and erogenous sensation in the neophallus is a goal of phalloplasty. Erectile function may also be addressed, either through the use of an erectile implant or by utilizing tissues with inherent erectile potential.
- Scrotal Construction:
-
- Phalloplasty often includes the creation of a scrotum. The appearance and positioning of the scrotum can influence the overall aesthetic outcome.
- Donor Site Appearance:
-
- The donor site, from which tissue is taken for constructing the neophallus (commonly the forearm or thigh), also impacts outcomes. Surgeons aim to minimize scarring and preserve function at the donor site.
- Postoperative Complications:
-
- Complications, though relatively rare, can occur. These may include issues such as wound healing problems, infection, or the need for additional revisions. Surgeons take measures to minimize these risks.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation:
-
- The recovery period after phalloplasty is significant for achieving optimal outcomes. Patients are typically provided with postoperative care instructions and may engage in rehabilitation exercises to enhance functionality.
- Patient Satisfaction:
-
- Patient satisfaction with the results of phalloplasty is a crucial measure of success. Open communication between the patient and the surgical team is essential in addressing expectations and achieving the desired outcomes.
- Follow-up Care:
-
- Regular follow-up appointments with the surgical team are essential for monitoring healing, addressing any concerns, and ensuring that the patient is satisfied with the long-term outcomes of the surgery.
It’s important to note that individual experiences and preferences can vary, and not all individuals choose to undergo or are eligible for phalloplasty. Moreover, advancements in surgical techniques continue to improve outcomes, and ongoing research aims to enhance both the aesthetic and functional aspects of phalloplasty for transgender individuals. As with any medical procedure, those considering phalloplasty should consult with experienced healthcare professionals to discuss their specific goals, expectations, and potential outcomes.
Metoidioplasty results
Metoidioplasty is a gender-affirming surgical procedure for individuals undergoing female-to-male (FTM) transition. This procedure involves releasing the clitoral ligaments to enhance the visibility and functionality of the clitoris, which has been naturally enlarged through hormone therapy. Metoidioplasty may also include urethral lengthening to allow for standing urination. Here are details on metoidioplasty results:
- Clitoral Enlargement:
- Metoidioplasty aims to maximize the visibility and functionality of the naturally enlarged clitoris resulting from testosterone therapy. The extent of clitoral enlargement varies among individuals and affects the overall size and appearance of the neophallus.
- Urethral Lengthening:
- Urethral lengthening is a common component of metoidioplasty, allowing individuals the ability to urinate while standing. The success of this aspect of the surgery influences functional outcomes.
- Aesthetic Appearance:
- The aesthetic appearance of the neophallus is a significant outcome of metoidioplasty. Surgeons work closely with patients to achieve a result that aligns with their desired size, shape, and appearance.
- Sensation:
- Metoidioplasty aims to preserve and enhance tactile sensation in the neophallus. The surgery involves releasing ligaments to allow the clitoris to be positioned in a more forward and prominent position.
- Erectile Function:
- Testosterone therapy contributes to clitoral enlargement, and some individuals may experience enhanced erectile function. While metoidioplasty does not typically involve the implantation of erectile devices, individuals may achieve some degree of erectile capacity.
- Scrotal Construction:
- Metoidioplasty may include scrotoplasty, where a scrotum is created. The appearance and positioning of the scrotum contribute to the overall aesthetic outcome.
- Postoperative Complications:
- Complications after metoidioplasty are relatively rare but can include issues such as wound healing problems, infection, or the need for additional revisions. Surgeons take measures to minimize these risks.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- The recovery period after metoidioplasty is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Patients are typically provided with postoperative care instructions and may engage in rehabilitation exercises to enhance functionality.
- Patient Satisfaction:
- Patient satisfaction with the results of metoidioplasty is a critical measure of success. Open communication between the patient and the surgical team is essential in addressing expectations and achieving the desired outcomes.
- Follow-up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments with the surgical team are essential for monitoring healing, addressing any concerns, and ensuring that the patient is satisfied with the long-term outcomes of the surgery.
Metoidioplasty is a viable option for individuals who prioritize maintaining genital sensation and functionality without the need for extensive tissue grafts. As with any gender-affirming surgery, it’s important for individuals considering metoidioplasty to consult with experienced healthcare professionals to discuss their specific goals, expectations, and potential outcomes.
Gender-affirming genital surgery
Gender-affirming genital surgery is a collective term that encompasses various surgical procedures designed to align an individual’s physical characteristics with their gender identity. These procedures are a crucial aspect of gender transition and are chosen by transgender and non-binary individuals seeking to affirm their gender. The specific surgeries differ between individuals assigned male at birth (AMAB) and individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB). Here are details on gender-affirming genital surgeries:
For Individuals Assigned Male at Birth (AMAB):
- Phalloplasty:
- Phalloplasty is a surgical procedure that involves the construction of a neophallus using tissues from different parts of the body (commonly the forearm or thigh). This surgery may also include scrotoplasty and the creation of a urethra for standing urination.
- Metoidioplasty:
- Metoidioplasty involves releasing the clitoral ligaments to enhance the visibility and functionality of the clitoris, which has been naturally enlarged through hormone therapy. Urethral lengthening may also be performed to allow for standing urination.
- Scrotoplasty:
- Scrotoplasty is a procedure to create a scrotum, either as part of phalloplasty or metoidioplasty. The scrotum may or may not include testicular implants.
- Urethral Lengthening:
- Urethral lengthening is often performed to allow individuals to urinate while standing. This can be part of both phalloplasty and metoidioplasty.
For Individuals Assigned Female at Birth (AFAB):
- Vaginoplasty:
- Vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure to create a neovagina using penile and scrotal tissues, or other graft options. The surgery aims to provide a functional and aesthetically pleasing vagina.
- Labiaplasty:
- Labiaplasty involves shaping and contouring the labia to create a more natural and feminine appearance. It is often performed as part of vaginoplasty.
- Clitoroplasty:
- Clitoroplasty is the creation or refinement of the clitoris to achieve a more natural and sensitive appearance. It is often part of vaginoplasty.
- Vulvoplasty:
- Vulvoplasty may be performed to create or enhance the external genitalia, including the labia and clitoris, for a more feminine appearance.
- Orchiectomy:
- Orchiectomy is the surgical removal of the testicles. While it does not create a neovagina, it is a surgical step that some individuals choose as part of their gender-affirming process.
General Considerations:
- Surgical Goals:
- The goals of gender-affirming genital surgery vary among individuals. Some prioritize aesthetic outcomes, while others emphasize functionality or the ability to engage in sexual activity.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- Recovery after gender-affirming genital surgery involves a healing period and rehabilitation exercises. Postoperative care instructions are provided to minimize complications and optimize outcomes.
- Patient Satisfaction:
- Patient satisfaction is a crucial aspect of gender-affirming surgeries. Open communication between the surgical team and the individual is essential to address expectations and concerns.
- Follow-up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor healing, address any complications, and ensure overall well-being.
- Mental Health Support:
- Access to mental health support is vital throughout the gender-affirming process, including before and after surgeries, to address psychological aspects and ensure holistic care.
Individuals considering gender-affirming genital surgery should consult with experienced healthcare professionals who specialize in transgender healthcare. The decision to undergo surgery is highly personal, and comprehensive care involves consideration of physical, emotional, and social well-being.
FTM genital reconstruction
Female-to-male (FTM) genital reconstruction, also known as bottom surgery or masculinizing genital surgery, is a gender-affirming surgical procedure that involves transforming the external genitalia to align with an individual’s male gender identity. There are several surgical options available, and the choice depends on factors such as individual preferences, anatomical considerations, and surgical goals. Here are details on some of the common procedures involved in FTM genital reconstruction:
- Phalloplasty:
- Phalloplasty is a surgical procedure that aims to create a neophallus (new penis). The surgeon typically uses tissues from other parts of the body, such as the forearm, thigh, or abdomen, to construct the neophallus. The procedure may involve urethral lengthening for standing urination, scrotoplasty for creating a scrotum, and the possibility of implanting erectile devices for sexual function.
- Metoidioplasty:
- Metoidioplasty involves releasing the ligaments around the enlarged clitoris (resulting from testosterone therapy) to make it more prominent. This procedure may also include urethral lengthening for standing urination, scrotoplasty, and other refinements to enhance the appearance and functionality of the genitalia.
- Scrotoplasty:
- Scrotoplasty is a procedure that creates a scrotum to house testicular implants or the patient’s own tissue. It is often performed as part of phalloplasty or metoidioplasty.
- Urethral Lengthening:
- Urethral lengthening is commonly included in both phalloplasty and metoidioplasty procedures. It allows the individual to urinate while standing, enhancing the overall functional aspect of the reconstructed genitalia.
- Hysterectomy and Salpingo-oophorectomy:
- Some individuals may choose to undergo a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) and salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries) as part of their gender-affirming process. These procedures are not directly related to external genital reconstruction but are often performed simultaneously or separately.
Considerations and General Information:
- Surgical Goals:
- The goals of FTM genital reconstruction vary among individuals. Some prioritize aesthetic outcomes, while others prioritize functionality or the ability to engage in sexual activity.
- Risk and Complications:
- As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications associated with FTM genital reconstruction. These can include infection, delayed wound healing, scarring, and changes in sensation. Surgeons discuss these risks with patients during the consultation process.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- Recovery after FTM genital reconstruction involves a healing period and rehabilitation exercises. Patients are provided with postoperative care instructions to minimize complications and optimize outcomes.
- Patient Satisfaction:
- Patient satisfaction is a crucial aspect of FTM genital reconstruction. Open communication between the surgical team and the individual is essential to address expectations and concerns.
- Follow-up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor healing, address any complications, and ensure overall well-being.
It’s important for individuals considering FTM genital reconstruction to consult with experienced healthcare professionals who specialize in transgender healthcare. The decision to undergo surgery is highly personal, and comprehensive care involves consideration of physical, emotional, and social well-being. Each individual’s journey is unique, and healthcare providers work collaboratively with patients to tailor the surgical plan to meet their specific goals and needs.
Female-to-male bottom surgery results
Female-to-male (FTM) bottom surgery, also known as gender-affirming genital surgery or masculinizing genital surgery, aims to create male-typical genitalia for individuals assigned female at birth. The results of FTM bottom surgery can vary based on the specific procedure chosen, individual anatomy, and surgical techniques. Here are details on the potential results of FTM bottom surgery:
- Phalloplasty Results:
- Phalloplasty involves creating a neophallus (new penis) using tissues from other parts of the body, such as the forearm, thigh, or abdomen. The size, appearance, and sensation of the neophallus can vary based on the chosen surgical technique, the amount of available donor tissue, and individual healing.
- Metoidioplasty Results:
- Metoidioplasty involves releasing the clitoral ligaments to enhance the visibility and functionality of the naturally enlarged clitoris resulting from testosterone therapy. The neophallus created in metoidioplasty is smaller than that in phalloplasty but is often more sensitive.
- Urethral Lengthening Results:
- Both phalloplasty and metoidioplasty often include urethral lengthening, allowing individuals to urinate while standing. The success of this aspect of the surgery influences functional outcomes.
- Scrotoplasty Results:
- Scrotoplasty is a procedure to create a scrotum to house testicular implants or the patient’s own tissue. The appearance and positioning of the scrotum contribute to the overall aesthetic outcome.
- Aesthetic Appearance:
- The aesthetic appearance of the genitalia after FTM bottom surgery is a significant aspect of the results. Surgeons work closely with patients to achieve a result that aligns with their desired size, shape, and appearance.
- Sensation:
- Sensation in the neophallus is an important aspect of FTM bottom surgery outcomes. The goal is to preserve and enhance tactile sensation to ensure a positive experience for the individual.
- Erectile Function (Phalloplasty):
- In phalloplasty, the potential for erectile function is often addressed through the use of erectile implants or tissues with inherent erectile potential. This aspect is discussed with the surgical team during the consultation process.
- Postoperative Scarring:
- Postoperative scarring is a natural part of the healing process. Surgeons aim to minimize scarring and may provide recommendations for scar management techniques to optimize aesthetic outcomes.
- Complications and Revisions:
- While complications are relatively rare, they can occur. Complications may include issues such as wound healing problems, infection, or the need for additional revisions. Surgeons take measures to minimize these risks and address any concerns.
- Patient Satisfaction:
- Patient satisfaction is a crucial measure of success in FTM bottom surgery. Open communication between the patient and the surgical team is essential in addressing expectations and achieving the desired outcomes.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- Recovery after FTM bottom surgery involves a healing period and rehabilitation exercises. Patients are provided with postoperative care instructions to minimize complications and optimize outcomes.
- Follow-up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor healing, address any complications, and ensure overall well-being.
Individuals considering FTM bottom surgery should consult with experienced healthcare professionals who specialize in transgender healthcare. The decision to undergo surgery is highly personal, and comprehensive care involves consideration of physical, emotional, and social well-being. Each individual’s journey is unique, and healthcare providers work collaboratively with patients to tailor the surgical plan to meet their specific goals and needs.
Neophallus appearance
The appearance of a neophallus, which is a surgically created penis resulting from procedures such as phalloplasty or metoidioplasty, can vary based on several factors, including the chosen surgical technique, individual anatomy, and the goals of the patient. Here are details on the potential appearance of a neophallus:
- Size:
- The size of the neophallus is a significant aspect of its appearance. The desired size is a personal choice made in consultation between the individual and the surgical team. Surgeons aim to achieve a size that aligns with the patient’s goals and expectations.
- Proportions:
- The proportions of the neophallus, including its length and girth, are considered to achieve a natural and aesthetically pleasing appearance. Proportions are individualized based on the patient’s preferences and anatomical considerations.
- Aesthetics:
- The aesthetic appearance of the neophallus is carefully crafted to resemble male genitalia. Surgeons work to create a phallic structure with well-defined contours, a defined glans, and a realistic appearance that aligns with the patient’s gender identity.
- Scrotum Appearance:
- If scrotoplasty is performed as part of the procedure, the appearance of the scrotum is considered. The scrotum is created to house testicular implants or the patient’s own tissue, contributing to the overall appearance of the genitalia.
- Urethral Opening:
- The placement and appearance of the urethral opening are important for functional outcomes, especially in surgeries that involve urethral lengthening. Surgeons aim to position the urethral opening in a way that allows for standing urination.
- Sensation:
- Preserving or enhancing sensation in the neophallus is an important goal. The extent of sensation can vary between individuals and is influenced by the chosen surgical technique.
- Scar Placement and Visibility:
- Postoperative scarring is a natural part of the healing process. Surgeons carefully plan incisions and suture lines to minimize scarring and optimize the overall appearance of the neophallus. Scar visibility can vary based on factors such as skin tone and individual healing.
- Hair Growth:
- In some cases, the neophallus may exhibit hair growth, especially if it is created using skin from a donor site with hair follicles (such as the forearm or thigh). The visibility and distribution of hair can be influenced by individual factors.
- Erectile Function (Phalloplasty):
- In phalloplasty, where erectile devices or tissues with inherent erectile potential may be used, the appearance during erection is considered. Surgeons discuss the potential for erectile function and its impact on the neophallus’s appearance with patients during the consultation process.
- Overall Symmetry:
- Achieving overall symmetry in the appearance of the neophallus is important for a natural and harmonious result. Surgeons carefully consider the placement and alignment of structures to achieve balanced aesthetics.
It’s crucial to note that individual experiences and preferences can vary, and the appearance of the neophallus is a highly personal aspect of the gender-affirming process. Open communication between individuals and their surgical team is essential to address expectations, discuss desired outcomes, and ensure a tailored approach that aligns with the individual’s goals and identity.
Satisfaction with FTM bottom surgery
Satisfaction with female-to-male (FTM) bottom surgery, also known as genital masculinization surgery, is a highly individualized and subjective experience. It is influenced by various factors, including the specific surgical procedures chosen, the skill of the surgical team, individual expectations, and postoperative outcomes. Here are key considerations regarding satisfaction with FTM bottom surgery:
- Communication and Expectations:
- Open and clear communication between the individual and the surgical team is crucial. Establishing realistic expectations about the outcomes, potential limitations, and the recovery process helps set the foundation for satisfaction.
- Choice of Surgical Procedures:
- The choice of specific surgical procedures, such as metoidioplasty or phalloplasty, can impact satisfaction. Individuals have different preferences, and the chosen procedures should align with the individual’s goals and desires.
- Aesthetic Results:
- Satisfaction often hinges on the aesthetic results of the surgery. The appearance of the neophallus, scrotum, and overall genital region is highly personal. Surgeons work to create results that align with the individual’s desired size, shape, and appearance.
- Functional Outcomes:
- Satisfaction is closely tied to functional outcomes, including the ability to urinate while standing, potential erectile function (in the case of phalloplasty), and overall functionality of the reconstructed genitalia.
- Sensation and Sexual Function:
- The preservation and enhancement of tactile sensation in the genital area are important factors. For individuals interested in sexual function, the satisfaction with the sensory and functional aspects of the neophallus can significantly contribute to overall well-being.
- Postoperative Scarring:
- The visibility and management of postoperative scarring can influence satisfaction. Surgeons aim to minimize scarring, and individuals may explore scar management techniques to optimize aesthetic outcomes.
- Recovery Experience:
- Satisfaction is also influenced by the overall experience during the recovery period. Adequate support, effective pain management, and adherence to postoperative care instructions contribute to a positive recovery experience.
- Complications and Revisions:
- While complications are relatively rare, their occurrence and the need for any revisions can impact satisfaction. Surgeons work to minimize risks, promptly address complications, and, if necessary, perform revisions to optimize outcomes.
- Quality of Life and Well-being:
- Satisfaction extends beyond the physical outcomes of surgery. Individuals often assess the impact on their overall quality of life, mental well-being, and self-esteem. Positive outcomes in these areas contribute to higher satisfaction.
- Follow-up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential. Ongoing support, addressing any concerns, and monitoring long-term outcomes contribute to overall satisfaction.
It’s important for individuals considering FTM bottom surgery to thoroughly discuss their goals, expectations, and concerns with experienced healthcare professionals specializing in transgender healthcare. The decision to undergo surgery is deeply personal, and comprehensive care involves addressing physical, emotional, and social aspects of well-being. Postoperative satisfaction can vary, but thorough communication, realistic expectations, and a supportive healthcare team contribute to positive outcomes.